
The 12 lead ECG is an essential tool in the management of all cardiac disorders. Demystifying this series of squiggles in order to come to a meaningful diagnosis is one of the great arts of modern medicine and one which this course is designed to develop.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) was a phrase first coined by Willem Einthoven in 1893. Over the next two decades he went on to perfect the tool and coined many of the phrases and nomenclature we still use today. The ECG examines electrical voltages detected from depolarising cardiac muscle and translates them into images for our interpretation. It records on standardised moving paper with temporal divisions demarcating 200ms of duration (large squares) or 40ms (small squares) for ease of interpretation. The size of each deflection on the ECG is also standardised with 1mV usually representing 1cm of movement on the ECG.
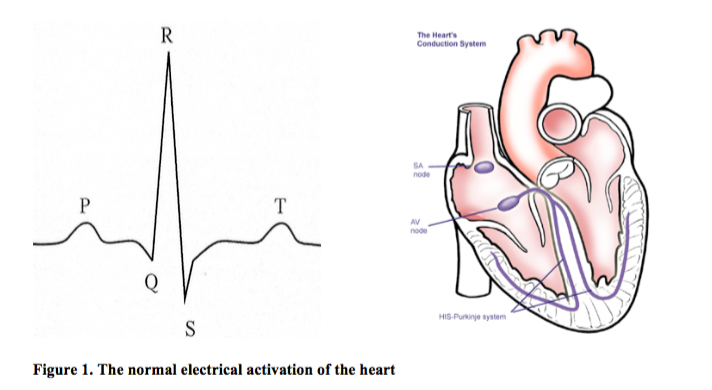
P waves represent atrial depolarisation. The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarisation, with the greater ventricular mass apparent in the greater size of complex. Atrial repolarisation is buried within this QRS and so is not seen. The repolarisation of the ventricle is seen as the T wave.
The PR interval demarcates the time taken for conduction to pass from the atria to the ventricles through the AV node. A short PR interval, that less than 0.12s (three small squares), represents abnormally rapid conduction and may indicate an area of additional, faster, conduction tissue between the atria and ventricles, known as an accessory pathway. A long PR interval (>0.2 s) represents delayed conduction through the AV node and is referred to as first degree heart block.
The QRS represents ventricular depolarisation and occurs through His-Purkinje fibres which have rapid conduction capabilities. Normal conduction takes less than 0.12s (three small squares) and any prolongation of this duration represents conduction block in the His- Purkinje system. These fibres divide to overly the left and right sides of the heart, forming two main bundles – the left bundle and right bundle – hence the phrase bundle branch block.

Supported by SimpleEducation.co