It has been considered that an interatrial block exists when there is a delay of conduction in some part of the Bachm ann’s bundle zone.1 The interatrial blocks are the most frequent and well-known blocks at atrial level. These are expressed in the electrocardiogram (ECG) by the presence of a P wave duration that equals or exceeds 120 milliseconds and presents usually a bimodal morphology, especially in leads I, II, VL or inferior leads. This represents partial IAB (P-IAB). If there is a P wave morphology ± in II, III, and VF with duration ≥120 ms, we speak about advanced interatrial block (A-IAB) (see Figure 1 )1-3 .
ann’s bundle zone.1 The interatrial blocks are the most frequent and well-known blocks at atrial level. These are expressed in the electrocardiogram (ECG) by the presence of a P wave duration that equals or exceeds 120 milliseconds and presents usually a bimodal morphology, especially in leads I, II, VL or inferior leads. This represents partial IAB (P-IAB). If there is a P wave morphology ± in II, III, and VF with duration ≥120 ms, we speak about advanced interatrial block (A-IAB) (see Figure 1 )1-3 .
Which are the P wave ECG Patterns that Meet the Criteria for Interatrial Block?
The P wave ECG Pattern of Interatrial Block May be Transient
The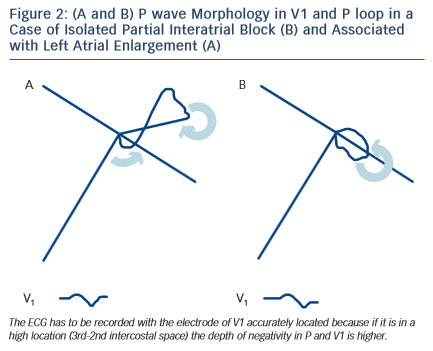 presence of transient deterioration of interatrial conduction, that is interatrial block, of first or third degree may appear in the same ECG recording on a beat-by-beat basis or in separate recordings. The first case may be considered as a part of the concept of atrial aberrancy, a term first coined by Chung4 in 1972, similar to ventricular aberrancy (see later)2,4.
presence of transient deterioration of interatrial conduction, that is interatrial block, of first or third degree may appear in the same ECG recording on a beat-by-beat basis or in separate recordings. The first case may be considered as a part of the concept of atrial aberrancy, a term first coined by Chung4 in 1972, similar to ventricular aberrancy (see later)2,4.
The P wave ECG Pattern of Interatrial Block May Appear without Associated Atrial Enlargement
The prolonged P wave duration (P-wave duration ≥120 milliseconds) may be present in the elderly but can also be a consequence of acute illness, such as pericarditis or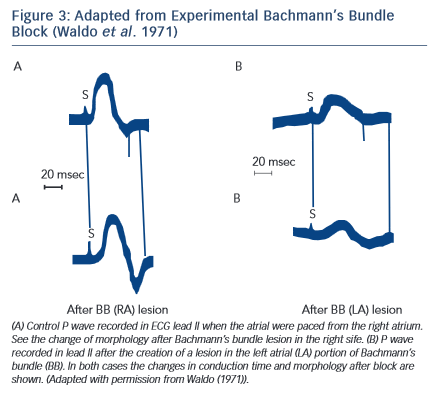 acute myocardial infarction without atrial enlargement (ECG pattern of partial interatrial block P-IAB). In fact, in these cases, the duration of P wave may be as long as in left atrial enlargement (LAE), but the P loop does not move so clearly backwards, as in a figure 8 shape, which results in a much smaller negative P wave component in lead V1 (see Figure 2). The combination of LAE with advanced interatrial block (A-IAB) (wide P wave ≥120 milliseconds and ± in leads,II, III, and VF) is very common but isolated cases of A-IAB may be seen. As the P wave often looks flat, to be accurate in the measurement in both types of IAB it is necessary to trace lines, as seen in Figures 4 and 6.
acute myocardial infarction without atrial enlargement (ECG pattern of partial interatrial block P-IAB). In fact, in these cases, the duration of P wave may be as long as in left atrial enlargement (LAE), but the P loop does not move so clearly backwards, as in a figure 8 shape, which results in a much smaller negative P wave component in lead V1 (see Figure 2). The combination of LAE with advanced interatrial block (A-IAB) (wide P wave ≥120 milliseconds and ± in leads,II, III, and VF) is very common but isolated cases of A-IAB may be seen. As the P wave often looks flat, to be accurate in the measurement in both types of IAB it is necessary to trace lines, as seen in Figures 4 and 6.
The P wave ECG Pattern May be Reproduced Experimentally (see Figure 3)
Experimental studies5 have demonstrated that cutting the Bachmann’s bundle at either the right or left atrial side results in a typical ECG pattern with wide P wave with biphasic ± morphology in inferior leads. It was also demonstrated6 that an attenuation of interatrial conduction, without affecting atrioventricular conduction, may occur after ablation of interatrial conduction zones along the right atrial septum. This intervention produces partial interatrial conduction block with an increase of P wave duration.