Bioresorbable Scaffolds
Table 2 shows the currently available BRS being tested in clinical trials. Poly L-lactic acid (PLLA) is the most commonly used material in BRS. PLLA is metabolised into carbon dioxide and water over a period of time (12–18 months), which is subsequently phagocytosed by the macrophages.23 ABSORB Bioabsorbable Vascular Scaffold (BVS) with a PLLA backbone releasing everolimus is the most widely investigated and the only approved bio-absorbable device (for de novo coronary lesions 2.0–3.8 mm in diameter).24 ABSORB Cohort A was an openlabel, prospective study of 30 patients with single de-novo lesions, which revealed acute recoil and late loss of scaffold area (-11.8 %) as measured by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) (corresponding an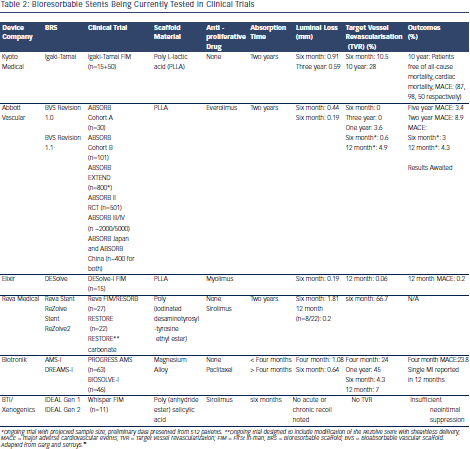 giographic in-stent loss of 0.44 mm) at six months.23 A follow-up study at two years using IVUS and optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed complete stent resorption, late luminal enlargement and absence of constrictive remodelling.25 Importantly, there was no incidence of ST at three years of follow-up and only one major adverse cardiac event (MACE) was reported at six months with no additional events at three years and five years of follow-up.26,27
giographic in-stent loss of 0.44 mm) at six months.23 A follow-up study at two years using IVUS and optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed complete stent resorption, late luminal enlargement and absence of constrictive remodelling.25 Importantly, there was no incidence of ST at three years of follow-up and only one major adverse cardiac event (MACE) was reported at six months with no additional events at three years and five years of follow-up.26,27
Early recoil observed in the ABSORB study led to Revision 1.1 with modifications allowing for a longer duration of radial support. This iteration is believed to allow more uniform drug delivery along with superior vessel wall support due to better strut distribution.28 A sixmonth analysis of this device in the ABSORB Cohort B trial showed encouraging results with late luminal loss of 0.19 mm, which is comparable to many current generation DES. The MACE rate was noted to be 10 % at three years without any scaffold thrombosis. In another substudy from Cohort B trial, the circumferential neointimal tissue growth did not cause any luminal compromise between six months and two years using OCT.25
The results of the large-scale non-randomised, single-arm trial evaluating the second iteration of the ABSORB BVS (ABSORB EXTEND) in ~1000 patients with longer lesions are expected in 2015. The preliminary results from 512 enrolled patients were noted to be promising with low ischaemia driven MACE and target vessel revascularisation (TVR) rates at 4.3 % and 4.9 % respectively at 12 months.29 In another randomised, single blind trial (ABSORB II), the ABSORB BVS will be tested against the everolimus DES, XIENCE.30 The ABSORB III trial is a non-inferiority trial (n~2,250) to evaluate one-year target lesion failure powered for non-inferiority against the XIENCE DES in subjects with up to two de novo native coronary artery lesions. In a second part of this trial (ABSORB IV), additional 3,000 patients would be recruited to study the primary end-point of patient reported angina at one-year and target lesion failure between 1–5 years.17 Results from separate randomised, non-inferiority trials comparing the safety and effectiveness of the ABSORB BVS in Japanese (ABSORB JAPAN) and Chinese (ABSORB CHINA) populations to the metallic XIENCE DES in ischaemic heart disease subjects are also awaited.31,32 Few clinical studies have evaluated the efficacy of ABSORB BVS in real-world practice. BVS were met with good in-hospital outcomes in the Polish absorb registry (POLAR) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) study with no mortality, myocardial infarction (MI) or ST reported in 88 patients enrolled.33 In another non-randomised study, patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) underwent BVS (n=150) implantation and were compared with controls receiving DES (n=103). Thirty-day and six-month MACE rates were noted to be similar between the two groups.34 BVS also showed promise with similar clinical outcomes as patients receiving DES in the PRAGUE-19 registry when used for primary PCI in ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) other than calcified and tortuous lesions.35 The results of an ongoing randomised trial (ABSORB STEMI: TROFI II study) designed to compare the neointimal healing score at six months in STEMI patients treated with ABSORB BVS and XIENCE DES are awaited.36
The first Poly (iodinated desaminotyrosyl-tyrosine ethyl ester) carbonate stent or REVA stent was met with high rate of target vessel revascularisation (TLR) secondary to mechanical failures.37 A redesigned version (ReZolve) with a more robust polymer with a sheathed delivery system (limiting its use in smaller vessels) was developed, which was again modified into ReZolve2 with a lower profile and sheathless delivery system being evaluated in the ongoing pilot study of the ReZolve™ airolimus-eluting bioresorbable coronary stent (RESTORE) trial.38
Although safety and radial strength of another bioresorbable stent, the IDEAL Poly (anhydride ester) salicylic acid stent39 were demonstrated in a 12-month follow up of a small (n=11) number of patients, the neointimal suppression was deemed to be insufficient due to low dose and rapid elution of sirolimus.40 A revised version with higher dose of sirolimus and optimised stent design with thinner struts is undergoing pre-clinical trials.
The initial iterations of non-drug eluting magnesium based absorbable scaffolds were met with disappointing results. The TVR rates were 39.7 % at four months and 45 % at 12 months due to both neointimal hyperplasia and recoil in the Clinical performance angiographic results of coronary stenting with absorbable metal stents (PROGRESS) AMS study.41 BIOSOLVE-I was the in-man trial to evaluate the efficacy of first paclitaxel-eluting absorbable magnesium based metal scaffold drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold (DREAMS). It demonstrated similar TVR rates as contemporary DES and everolimus-eluting BRS though it did not match the late lumen results noted with either platform.42