Adequate Patient Selection is Key to Ensure Success and Benefit of Coronary CTO PCI
Dr Gerald Werner from the Darmstadt Hospital (Germany) discussed the importance of patient selection in the PCI of coronary CTOs. Several questions should be addressed in the assessment of whether a patient with CTO will benefit from PCI. Is the patient symptomatic in terms of angina, dyspnoea or exercise limitation? Is there evidence of a prior MI? Accordıng to the EuroCTO club consensus document, recanalization of CTOs is ındıcated ın symptomatıc patıents that have no hıstory of prevıous MI. In case of prevıous MI viability should be documented ın the area provıded by the occluded artery and the myocardium at risk should be more than 10 %.7
In terms of predicting patient benefıt, the Euro CTO recommendations state that we should treat patients with CTO as any other CAD patients, provided the operator ıs experienced enough and that that the expected success rates are ın the range of 80 %. In a metaanalysis of CTO recanalisation, successful attempts were associated with symptomatic relief.8 Ischaemic burden is also reduced following PCI of CTO, and the decrease is greater at higher ischaemic burden. Conversely, in patients wıth a lower ischaemic burden, the treatment benefıt was less consıdering the pre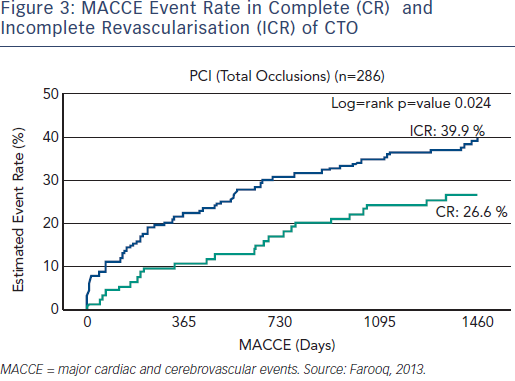 sence of potential complıcations and treatment costs related to the procedures.9 It has been suggested that in the setting of CTO, we should select patients for PCI with ischaemic burden >10 % of myocardium, to achieve certain benefit.9 Individual patient data should be always taken into account.
sence of potential complıcations and treatment costs related to the procedures.9 It has been suggested that in the setting of CTO, we should select patients for PCI with ischaemic burden >10 % of myocardium, to achieve certain benefit.9 Individual patient data should be always taken into account.
In multi-vessel disease and CTO, it is necessary to determine which lesion causes the symptoms, and also to obtain evidence of ischaemic burden and expected completeness of revascularisation. In the SYNTAX trıal ıncomplete revascularisation is associated with an increased rate of major cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE, see Figure 3) and the presence of CTOs is an ımportant contributor to the ıncomplete revascularısatıon.10 The residual SYNTAX score ıs an angıographıc tool that can quantıtate the level of the completeness of revascularisation. A residual SYNTAX Score exceeding eight was associated with high mortality (35.3 % all-cause mortality at five-years, p<0.001).11
Current treatment paradigms suggest that one or two vessel disease favours PCI while three-vessel disease requires surgery if complete revascularisation cannot be achieved with PCI. So, what if we can achieve complete revascularisation? This needs to be built into the guidelines. The strategy of the EuroCTO club in multi-vessel disease with CTO, is a staged procedure for non-CTO first, with the goal of complete revascularisation.
The publication of the article was supported by Alvimedica.