Advantages of Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Reproducibility and Accuracy
It has been found that HBPM readings are often lower than readings taken in the office and closer to the average BP recorded during 24-hour ABPM.22 HBPM allows increased numbers of readings, achieves more reproducible readings than office readings and provides improved correlations with measures of target organ damage.16,23–26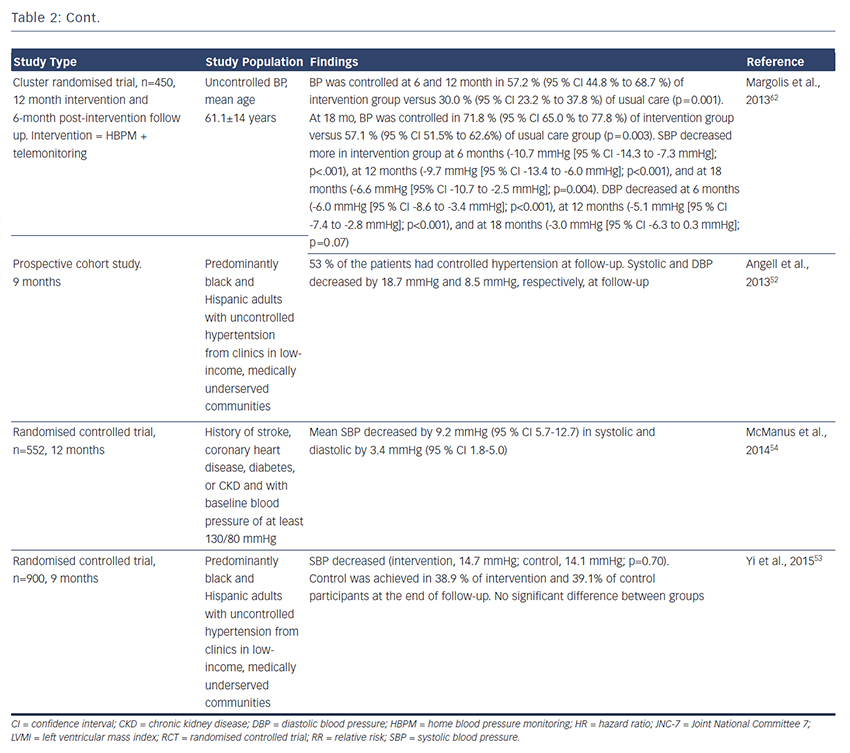
A randomised controlled trial (n=555) compared manual BP measurement and automated measurement in an office setting and concluded that the quality and accuracy of automated office BP measurement was significantly higher compared with manual office BP measurement.27 A retrospective analysis of a clinical trial (n=163) compared the withinpatient variability of the different methods of BP measurement for at least 6 weeks and found coefficients of variation of 8.6 %, 5.5 %; and 4.2 % for office BPM, ABPM and HPBM, respectively. The study concluded that a week of self-monitoring was the most accurate method of measuring BP.28 Another study (n=133) found that HBP has superior reproducibility compared with both office BPM and ABPM.29
White-coat Effect and Masked Hypertension
White-coat effect, defined as elevated office and low ambulatory or home BP, can manifest with very high clinic readings. The use of automated BP measurements have significantly reduced this effect in primary care settings.27 The reverse phenomenon – i.e. normal clinic BP and elevated out-of-clinic BP – is termed masked hypertension and is associated with increased CV risk.30,31 Some studies have found that HBPM is as effective as and more convenient than ABPM in the diagnosis of this phenomenon,32,33 but others suggest that ABPM has greater sensitivity.34 A recent meta-analysis found that HPBM is particularly useful in risk stratification in masked hypertension.31 Both phenomena are relatively common, occurring in 10–15 % of patients with hypertension, but diagnosis requires physicians to be alert to the possibility, particularly with regard to masked hypertension.30,35 The European Society of Hypertension has recommended that both white-coat and masked hypertension can be diagnosed using ambulatory or home BP measurements.17
Prediction of Cardiovascular and Stroke Morbidity and Mortality
Many,24,26,36–39 but not all,40,41 prospective studies have found that HBPM predicts CV and stroke42 morbidity and mortality more accurately than office BP; the major studies are summarised in Table 2. A meta-analysis included 5,008 people who had home and conventional BP measurements and were not being treated with antihypertensive medication that would influence the prognostic outcome. Participants were stratified into five categories of BP: optimal, 120/80 mmHg; normal, 120–129/80–84 mmHg; high–normal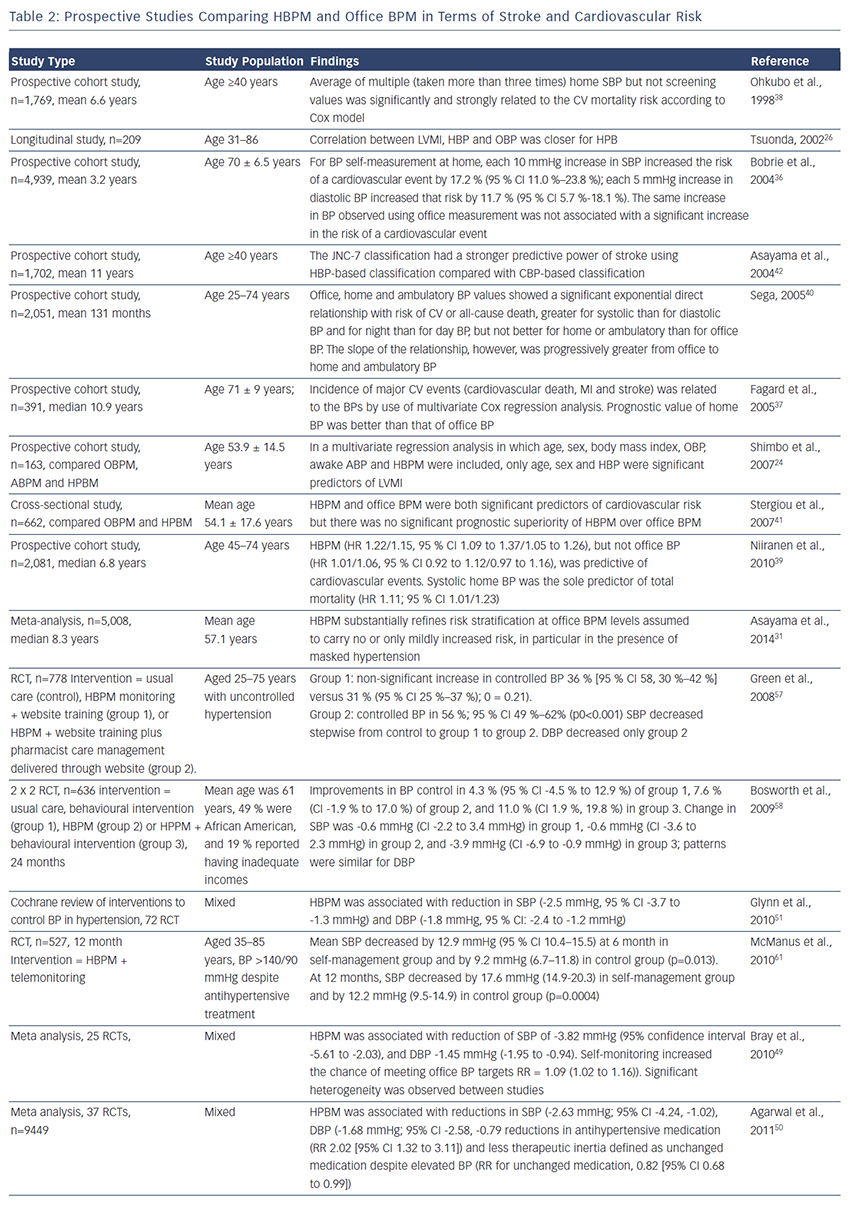 , 130–139/85–89 mmHg; mild hypertension, 140–159/90–99 mmHg; and severe hypertension, ≥160/≥100 mmHg. At every level of BP below severe hypertension, the additional measurements obtained from HBPM improved risk stratification, supporting the use of HBPM in routine assessment of risk.31 This finding could refine risk stratification in people with optimal, normal or high-normal BP, who are not conventionally treated. A recent systematic review (19 studies) compared HBPM with ABPM in terms of outcomes including heart attack, stroke, kidney failure and/or all-cause mortality and concluded that HBPM encourages patient-centred care and improves BP control and patient outcomes.43
, 130–139/85–89 mmHg; mild hypertension, 140–159/90–99 mmHg; and severe hypertension, ≥160/≥100 mmHg. At every level of BP below severe hypertension, the additional measurements obtained from HBPM improved risk stratification, supporting the use of HBPM in routine assessment of risk.31 This finding could refine risk stratification in people with optimal, normal or high-normal BP, who are not conventionally treated. A recent systematic review (19 studies) compared HBPM with ABPM in terms of outcomes including heart attack, stroke, kidney failure and/or all-cause mortality and concluded that HBPM encourages patient-centred care and improves BP control and patient outcomes.43
Large-scale studies are now investigating the optimum use of HBPM in prevention of CV outcomes. The multicentre Hypertension Objective Treatment Based on Measurement by Electrical Devices of Blood Pressure (HOMED-BP; 2001–2010) trial (n=3,518) proved the feasibility of adjusting antihypertensive drug treatment via a computer algorithm that automatically generated treatment recommendations based on HBP and suggested that a systolic HBP level of 130 mmHg should be an achievable and safe target.44 The Home Blood Pressure Measurement With Olmesartan Naive Patients to Establish Standard Target Blood Pressure (HONEST) study, a prospective observational study (n=21,591), found that morning HBP should be controlled to <145 mmHg.45
Other Advantages
Different methods of measuring BP response might clinically influence treatment decisions. A meta-analysis of more than 6,000 patients found that antihypertensive response to therapy measured by HBPM was 20 % less than office measurements.46 In addition, a clinical study found that HBPM was similar to 24-hour ABPM in assessing BP response to the antihypertensive agents atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide.47 Office BP measurements overestimated BP response compared with HBPM, with an average 4.6 mmHg greater reduction in SBP (p<0.0001) and 2.1 mmHg greater reduction in diastolic BP (p<0.0001) across all therapies.47 These findings indicate that HBPM can influence management decisions in hypertension, particularly given the relative ease of incorporating HBPM into daily activities.