IMAP IVUS
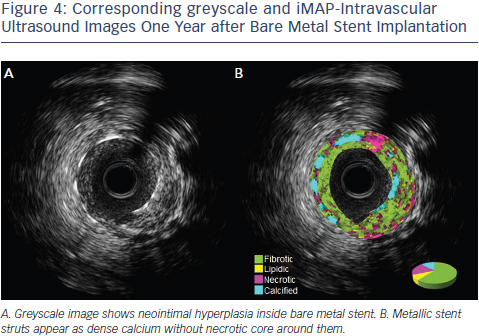
Another IVUS RF data analysis system is the iMAP software.25 Unlike VH-IVUS, iMap uses a 40 MHz single rotational t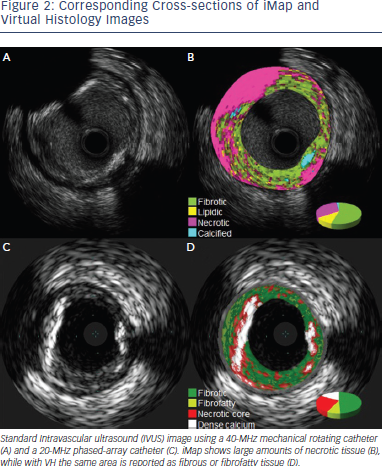 ransducer and can acquire RF data continuously, while VH-IVUS data are collected with a 20 MHz electronic catheter that acquires only electrocardiogramgated data. VH-IVUS uses autoregressive modelling to analyse the IVUS RF spectrum, while iMap uses a pattern recognition algorithm on the spectra that were obtained from a fast Fourier transformation and a histology-derived database. iMAP-IVUS classifies coronary plaque into four components (fibrotic, lipidic, necrotic, and calcified). Like VH-IVUS, iMAP could be used to detect high risk plaques and predict adverse events following PCI, for example, slow flow. However it is noteworthy that in vivo comparison of iMAP and VH-IVUS tissue characterisation has reported a significant and systematic variability in plaque composition estimates (See Figure 2). iMap expressed plaque as necrotic core in poor signal areas, such as guidewire artefact or acoustic shadowing of the calcium. VH-IVUS classified acoustic shadowing as fibrous or fibrofatty tissue. VH-IVUS showed metallic stent struts as dense calcium and necrotic core, while iMap showed thinner stent thickness without necrotic core around the stent (See Figures 3 and 4).26
ransducer and can acquire RF data continuously, while VH-IVUS data are collected with a 20 MHz electronic catheter that acquires only electrocardiogramgated data. VH-IVUS uses autoregressive modelling to analyse the IVUS RF spectrum, while iMap uses a pattern recognition algorithm on the spectra that were obtained from a fast Fourier transformation and a histology-derived database. iMAP-IVUS classifies coronary plaque into four components (fibrotic, lipidic, necrotic, and calcified). Like VH-IVUS, iMAP could be used to detect high risk plaques and predict adverse events following PCI, for example, slow flow. However it is noteworthy that in vivo comparison of iMAP and VH-IVUS tissue characterisation has reported a significant and systematic variability in plaque composition estimates (See Figure 2). iMap expressed plaque as necrotic core in poor signal areas, such as guidewire artefact or acoustic shadowing of the calcium. VH-IVUS classified acoustic shadowing as fibrous or fibrofatty tissue. VH-IVUS showed metallic stent struts as dense calcium and necrotic core, while iMap showed thinner stent thickness without necrotic core around the stent (See Figures 3 and 4).26
iMAP can be used for the in vivo identification of vulnerable plaque and prediction of adverse events of PCI. In a study of 87 patients, iMAP analysis revealed that the culprit plaques in patients with ACS contained larger lipidic and necrotic components with a smaller fibrous component compared to non-ACS group.27 In a study of 63 ST elevation MI patients, iMAP-IVUS imaging was performed in the culprit segment and the segment immediately proximal to the culprit lesion (non-culprit). At index procedure the culprit lesion had a higher percentage of necrotic tissue compared to the non-culprit lesions. At 10 months follow-up the proportion of necrotic tissue in the non-culprit lesion remained stable, but the percentage of lipidic tissue decreased.28 Like in studies with VH-IVUS, the necrotic plaque volume and necrotic plaque ratio by iMAP are predictors of slow flow during PCI.29
iMAP-IVUS has been used to evaluate neointimal tissue components after stent implantation. In a series of 61 lesions, iMAP-IVUS showed that neointima after drug eluting stent implantation consisted of statistically significant smaller fibrotic component, larger necrotic and calcified components compared with bare metal stent.30
Integrated Backscatter IVUS
Integrated backscatter IVUS (IB-IVUS) also uses a 40 MHz single rotational transducer.31 It analyses the RF signals by applying a fast Fourier transformation. It has been used for assessment of vulnerable plaques. IB-IVUS studies have demonstrated that culprit lesions as well as nonculprit lesions of acute coronary syndrome are significantly associated with the increase in lipid component and decrease in fibrous component compared to those with stable angina pectoris.32 The percentage of coronary lipid volume is independent predictor of no-reflow during PCI.33 In a study of 260 patients, large lipid volume (odds ratio 1.95, 95 % confidence interval 1.14-3.33, P = 0.02) was significantly and independently associated with major adverse events defined as death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and any repeat revascularisation during median follow-up of 1285 days after drug eluting stent implantation.34 Serial IB-IVUS studies have demonstrated that statin therapy in patients with ACS reduces plaque volume and lipid components and increases in fibrous tissue content suggesting that statin therapy is able to induce plaque morphologic changes.35