Scenario IV – Stent Deployment and Malapposition
Optimal stent deployment is an important aspect of successful PCI because it has been well documented that stent mal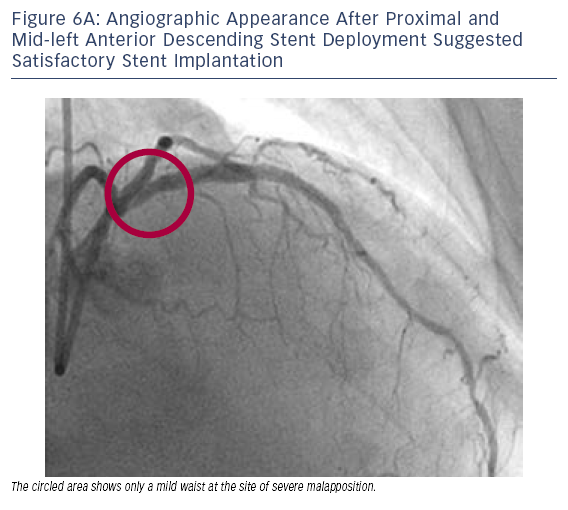 apposition can lead to subsequent stent thrombosis. The superior resolution of OCT (10–20 μm) gives it the distinct advantage of being able to reveal other vascular details that are beyond the capacity of IVUS (100–150 μm), such as tissue prolapse between stent struts or distal edge dissection.
apposition can lead to subsequent stent thrombosis. The superior resolution of OCT (10–20 μm) gives it the distinct advantage of being able to reveal other vascular details that are beyond the capacity of IVUS (100–150 μm), such as tissue prolapse between stent struts or distal edge dissection.
Case 6
Age: 62
Gender: Male
History: Prior myocardial infarction, controlled hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, a family history of coronary artery disease and prior stroke. Presented with CCS Class II angina while receiving two antianginal medications (verapamil and longacting nitrate).
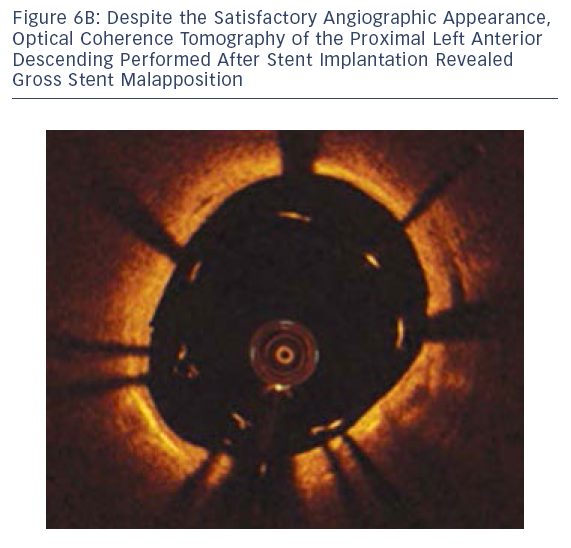 aled g
aled g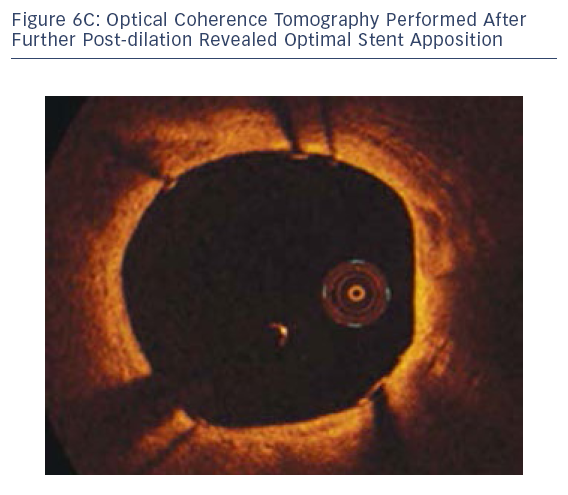 ross stent malapposition (see Figure 6B).
ross stent malapposition (see Figure 6B).In this case, OCT was able to diagnose stent malapposition and was used to guide the post-dilation strategy. OCT also confirmed optimal final stent apposition.
The publication of this information was supported by St. Jude Medical.